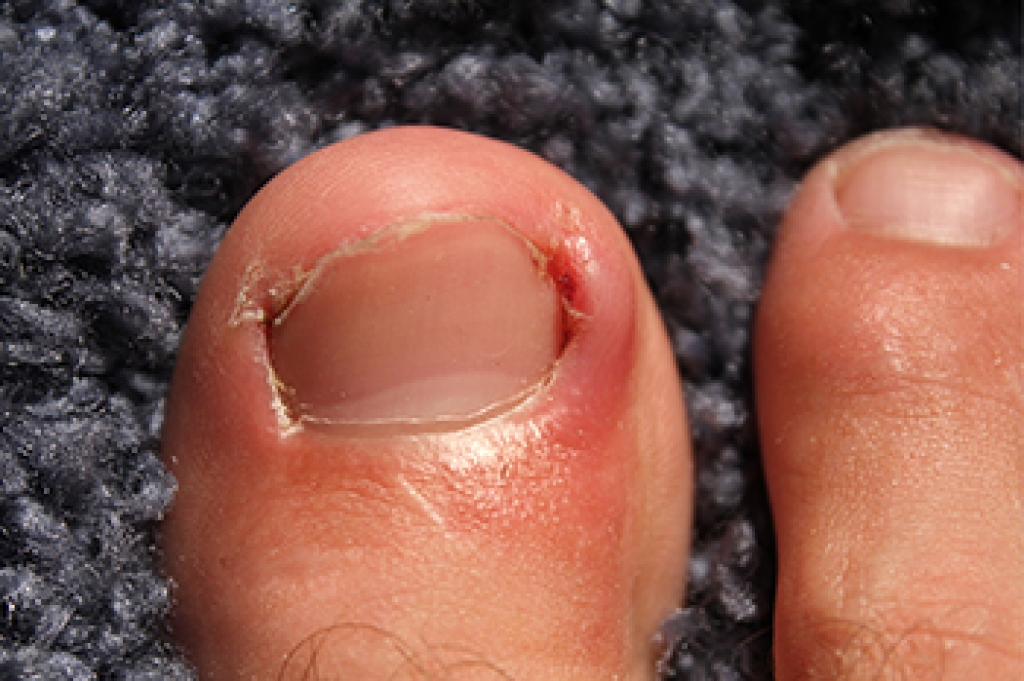
Ingrown toenails develop when the nail grows into the surrounding skin, or when the skin grows over the edge of the nail. A primary cause of ingrown toenails is improper nail trimming, such as cutting the nail and rounding the edges instead of cutting straight across. This may result in the nail curling under and digging into the skin, which often results in pain as well as potential for infection. Other risk factors for ingrown toenails are wearing shoes that squeeze the toes, engaging in activities that put pressure on the feet, and having foot abnormalities like bunions or hammertoes. People with a family history of ingrown toenails, diabetes, or poor circulation are also more susceptible. Symptoms often include redness, swelling, and pain, and if untreated, can progress to infection. A podiatrist can assess and treat the condition, using techniques to relieve pain and in severe cases removing part of the nail or nail bed. If you have a painful or infected ingrown toenail, it is suggested that you schedule an appointment with a podiatrist.
Ingrown toenails may initially present themselves as a minor discomfort, but they may progress into an infection in the skin without proper treatment. For more information about ingrown toenails, contact Elie C. Daniel, DPM of Illinois. Our doctor can provide the care you need to keep you pain-free and on your feet.
Ingrown Toenails
Ingrown toenails are caused when the corner or side of a toenail grows into the soft flesh surrounding it. They often result in redness, swelling, pain, and in some cases, infection. This condition typically affects the big toe and may recur if it is not treated properly.
Causes
- Improper toenail trimming
- Genetics
- Improper shoe fitting
- Injury from pedicures or nail picking
- Abnormal gait
- Poor hygiene
You are more likely to develop an ingrown toenail if you are obese, have diabetes, arthritis, or have any fungal infection in your nails. Additionally, people who have foot or toe deformities are at a higher risk of developing an ingrown toenail.
Symptoms
Some symptoms of ingrown toenails are redness, swelling, and pain. In rare cases, there may be a yellowish drainage coming from the nail.
Treatment
Ignoring an ingrown toenail can have serious complications. Infections of the nail border can progress to a deeper soft-tissue infection, which can then turn into a bone infection. You should always speak with your podiatrist if you suspect you have an ingrown toenail, especially if you have diabetes or poor circulation.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our offices located in Princeton, Peru, and Mendota, IL . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.
